Blog
T-Ratios & Identities
- August 10, 2020
- Category: T-Ratios & Identities
☼ Definitions & Review of Concepts :
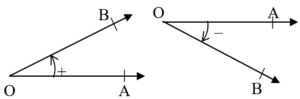
■ Angle : When a ray OA rotates about the point O from its initial position OA to find position OB, we say that ∠ AOB has been formed.
OA is called the initial side and OB, the terminal side of ∠AOB.
■ Positive & Negative Angles : When the ray OA rotates in anticlockwise direction, a positive angle is formed, and when it moves in clockwise direction, a negative angle is formed.
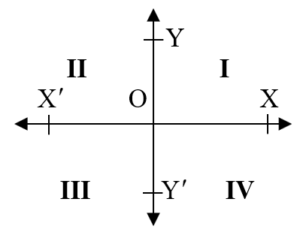
■ Quadrants : Let OX and YO be two lines at right angles to each other. We call OX and YO as x – axis and y – axis respectively.
These lines divide the plane into 4 parts.
The parts XOY, YO, O and OX are known as 1st, 2nd , 3rd and 4th quadrant respectively.
An angle is said to be in a particular quadrant, if the terminal side of the angle lines in that quadrant.
■ Measurement of Angles : Mainly there are three system for measuring angles.
▪ Hexadecimal system : In this system, angle is measured in degrees.
1 right angle = 90o, 1o = 60′ and = 60″
▪ Centesimal ( or Decimal ) system : In this system angle is measured in grades.
1 right angle = 100g, 1g = and
= 100″.
▪ Circular Measure : In this system, angle is measured in radians.
The angle is subtended at the centre of a circle by an arc of length equal to its radius is 1 radian, written as 1c.
= 180o = 200g = 2 right angles.
