Blog
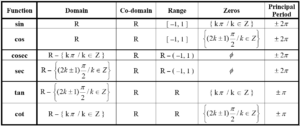
Domain Range Co-domain Zeros and Principal Period of Trigo Functions : -
- August 11, 2020
- Category: Domain Range Co-domain Zeros and Principal Period of Trigo Functions : -
☼ Domain, Range, Co-domain, Zeros and Principal Period of Trigo. Functions : –
First Quadrant
sin = cos θ sin (
) = sin θ
cos = sin θ cos (
) = cos θ
tan = cot θ tan (
) = tan θ
Second Quadrant
sin = cos θ sin (
) = sin θ
cos = – sin θ cos (
) = – cos θ
tan = – cot θ tan (
) = – tan θ
Third Quadrant
sin = – cos θ sin (
) = – sin θ
cos = – sin θ cos (
) = – cos θ
tan = cot θ tan (
) = tan θ
Fourth Quadrant
sin = – cos θ sin (
) = – sin θ
cos = sin θ cos (
) = cos θ
tan = – cot θ tan (
) = – tan θ
* Some Results : –
1) Where,
= an angle measured in degree.
= a length of an arc measured in radian.
2) sin2α – sin2β = cos2 β – cos2 α = sin (α + β) sin (α – β)
cos2α – sin2 β = cos2 β – sin2 α = cos (α + β) cos (α – β)
3) Range of f (α) = cos α + b sin β is , where r =
4) 2 sin α cos β
= sin() + sin (
)
2 cos α sin β
= sin() – sin (
)
2 cos α cos β
= cos() + cos (
)
2 sin α sin β
= cos () – cos(
)
= – cos () + cos(
)
sin C + sin D = 2 sin cos
sin C – sin D = 2 cos sin
cos C + cos D = 2 cos cos
cos C – cos D = – 2 sin sin
5) sin 2 α = 2 sin α cos α
= cos 2 α = cos2 α – sin2 α
= 2 cos2 α – 1
= 1 – 2sin2 α
=
tan 2 α =
6) sin2 α =
2 sin2 α = 1 – cos 2 α cos2 α =
2 cos 2 α = 1 + cos 2
tan2 α =
7) sin 3 α = 3 sin α – 4 sin3 α
cos 3 α = 4 cos3 α – 3 cos α
tan 3 α =
8) sin 150 = cos 750 =
tan 150 = cot 750 = 2 –
sin 180 = cos 720 =
sin 360 = cos 540 =
sin 750 = cos 150 =
tan 750 = cot 150 = 2 +
sin 720 = cos 180 =
sin 540 = cos 360 =
9) tan 22 = cot 67
=
sin 22 = cos 67
=
tan 67 = cot 22
=
+ 1
sin 67 = cos 22
=
10) sin-1 (– x ) = – sin-1 x ;
cosec-1 (– x ) = – cosec-1 x ;
tan-1 (– x ) = – tan-1 x ;
cos-1 (– x ) = π – cos-1 x ;
sec-1 (– x ) = π – sec-1 x ;
cot-1 (– x ) = π – cot-1 x ;
11) cosec-1 x = sin-1 ;
sec-1 x = cos-1 ;
cot-1 x = tan-1 ; x > 0
= π + tan-1 ; x < 0
12) sin-1 x + cos-1 x = ;
sec -1 x + cosec -1 x = ;
13) If x > 0 and y > 0, then
tan-1 x + tan-1 y = tan-1 ; xy < 1
tan-1 x + tan-1 y = \pi + tan-1 ; xy > 1
tan-1 x + tan-1 y = ; xy = 1
tan-1 x – tan-1 y = tan-1
14) sin-1 x = cos-1 = tan-1
; 0 < x < 1
cos-1x = sin-1 = tan-1
; 0 < x < 1
tan-1 x = cos-1 = sin-1
; x > 0
tan -1 x + cot -1 x = ;
15) The solution of sin θ = 1 is ; [ i.e. P (B) = P ( 0, 1 ) ]
The solution of sinθ = –1 is ; [ i.e. P (
) = P ( 0, –1 ) ]
The solution of cos θ = 1 is ; [ i.e. P (A) = P ( 1, 0 ) ]
The solution of cos θ = –1 is ; [ i.e. P (
) = P (–1, 0) ]
16) The solution of cos θ = a, is
The solution of sin θ = a, is
The solution of tan θ = a, is
17) The solution of a cos θ + b sin θ = c is { 2k π cos-1 + α / k Z }
Where, c2 r2 and r2 = a2 + b2
α [ 0, 2 π]
α is found from cos α = and sin α =
18) Triangle, In-circle and Circum-circle :-
s = length of semi-perimeter of a triangle
=
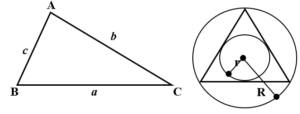
R = Circum-radius of a triangle
r = In-radius of a triangle
= Area of a triangle
In ABC,
( The length of an arc on unit circle corresponding to an angle is measured in radian )
Symbolically,m∠ BAC = A
m∠ ABC = B
m∠ BCA = C
BC = a
AC = b
AB = c
19) Sine – Rule :-
20) Cosine – Rule :-
cos A =
cos B =
cos C =
21) The Projection Rule :-
a = b cos C + c cos B
b = c cos A + a cos C
c = a cos B + b cos A
22) Napier’s Formula :-
23) Formulae for semi-angle ( Half-angle formulae ) :-
24) The area of ( The area of ABC ) :-
25) Formulae for In-radius :-
r =
r =
r =
r = =
r =
26) In ABC ( if A + B + C =
), then
sin 2A + sin 2B + sin 2C = 4 sin A sin B sin C
sin2 B + sin2 C – sin2 A = 2 sin B sin C cos A
cos A + cos B + cos C = 1 + 4 sin sin
sin
tan A + tan B + tan C = tan A tan B tan C
